ETHNICITY AND RACE
Differences between each of us are related to our customs, beliefs, values, habits.
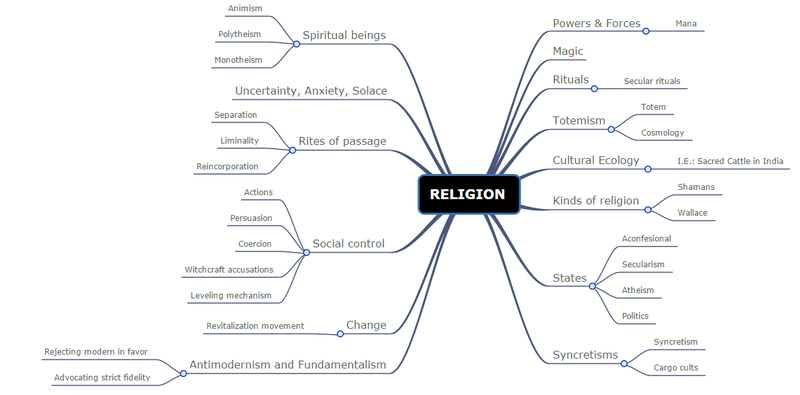
Our differences can come from our religion, race, ethnicity too.
A Paleontologist, Stephen Jay, explain the history of the race.
Evolution/ Creation - Concept of Race -The Race Of The First Man
This table is a very good global view of the difference between the race & ethnicity:
Comparison chart
Ethnicity |
Race | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An ethnic group or ethnicity is a population of human beings whose members identify with each other, on the basis of a real or a presumed common genealogy or ancestry. | The term race refers to the concept of dividing people into populations or groups on the basis of various sets of physical characteristics (which usually result from genetic ancestry). |
| Significance | Ethnicity connotes shared cultural traits and a shared group history. Some ethnic groups also share linguistic or religious traits, while others share a common group history but not a common language or religion. | Race presumes shared biological or genetic traits, whether actual or asserted. In the early 19th century, racial differences were ascribed significance in areas of intelligence, health, and personality. There is no evidence validating these ideas. |
| Genealogy | Ethnicity is defined in terms of shared genealogy, whether actual or presumed. Typically, if people believe they descend from a particular group, and they want to be associated with that group, then they are in fact members of that group. | Racial categories result from a shared genealogy due to geographical isolation. In the modern world this isolation has been broken down and racial groups have mixed. |
| Distinguishing Factors | Ethnic groups distinguish themselves differently from one time period to another. They typically seek to define themselves but also are defined by the stereotypes of dominant groups. | Races are assumed to be distinguished by skin color, facial type, etc. However, the scientific basis of racial distinctions is very weak. Scientific studies show that racial genetic differences are weak except in skin color. |
| Nationalism | In 19th century, there was development of the political ideology of ethnic nationalism -- creating nations based on a presumed shared ethnic origins (e.g. Germany, Italy, Sweden...) | In 19th century, the concept of nationalism was often used to justify the domination of one race over another within a specific nation. |
| Legal System | In the last decades of the 20th century, in the U.S. and in most nations, the legal system as well as the official ideology prohibited ethnic-based discrimination. | In the last decades of the 20th century, the legal system as well as the official ideology emphasized racial equality. |
| Conflicts | Often brutal conflicts between ethnic groups have existed throughout history and across the world. But most ethnic groups in fact get along peacefully within one another in most nations most of the time. | Racial prejudice remains a continuing problem throughout the world. However, there are fewer race-based conflicts in the 21st century than in the past. |
| Examples of conflict | Conflict between Tamil and Sinhalese populations in Sri Lanka. | Conflict between white and African-American people in the U.S., especially during the civil rights movement. |
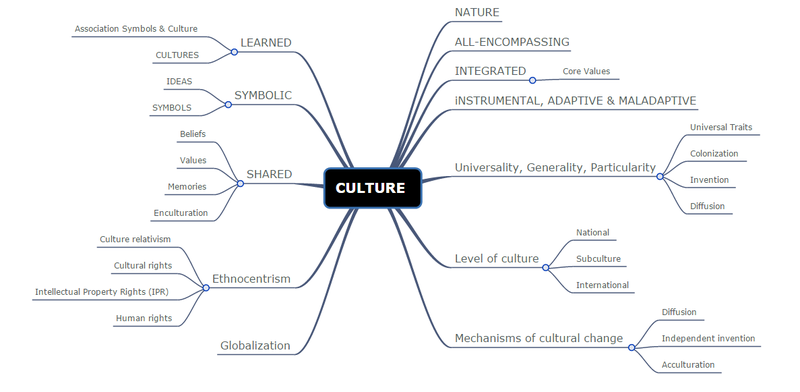
CULTURE & DIVERSITY
Culture is a word at several definitions: beliefs, customs, way of life, natural, education etc
We doesn't have a culture, we learn it, we build it, we recognize it.
The exact definition of the dictionnary is:
The totality of socially transmitted behavior patterns, arts, beliefs, institutions, and all other products of human work and thought.
Our culture learning depends on the uniquely developed human capacity to use symbols, signs that have necessary or natural connection to the things they stand for or signify.
Moreover you can share your culture and you can discover different culture than yours in the world.
A symbol of a culture can be the language, the food, the physical appearance (they are called our core values these one).
You can adapt your culture too, but hopefuly there are some generalities and universalities like the wedding or the music.

Unfortunately it exists some ethoncentrism and people very close. It means like you see your culture as superior and to apply values in judging the behavior and beliefs of people raised in other cultures.
The contrary of this idea is the cultural relativism: Cultural relativism is the view that all beliefs, customs, and ethics are relative to the individual within his own social context. In other words, “right” and “wrong” are culture-specific; what is considered moral in one society may be considered immoral in another, and, since no universal standard of morality exists, no one has the right to judge another society’s customs.
This video of 10min should be link with our course because this is very well explain and simple to memorize the concept of cultural relativism.
ANTHROPOLOGY
The anthropology is the science of human beings;
but more precisely the study of human beings and their ancestors through time and
space and in relation to physical character, environmental and social relations, and culture.
This is how we can see the diversity of customs, traditions and the richness of a population.
There are 4 differents subdisciplines of Anthropology:
- Sociocultural anthropologists examine social patterns and practices across cultures, with a special interest in how people live in particular places and how they organize, govern, and create meaning.
- Biological anthropologists seek to understand how humans adapt to diverse environments, how biological and cultural processes work together to shape growth, development and behavior, and what causes disease and early death.
- Archaeologists study past peoples and cultures, from the deepest prehistory to the recent past, through the analysis of material remains, ranging from artifacts and evidence of past environments to architecture and landscapes.
- Linguistic anthropology is the comparative study of ways in which language reflects and influences social life.
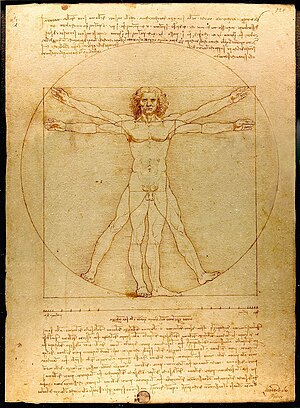
This plan of Leonard Da Vinci, "Vitruvian Man", is the first plan of the anthropology, drawing around 1490.
A profesor, David Crawford explains in 2min the Modern Culture and the Anthropology of the Human Being (very simple and well explained)
HUMAN RIGHTS & FUNDAMENTAL RIGHTS
The Human Rights and the Fundamental Rights are first of all declaration of law, most of them can be found in the
Universal Declaration of Human Rights
(http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Universal_Declaration_of_Human_Rights)
writted by the United Nations in 1948.
Fundamental rights are similar to human rights but are different in the sense that they have legal obligations and are enforceable in a court of law but human rights do not have such legal obligations and are not enforceable in courts.

Instead of the fundamental rights that they are generally regarded set of legal protections in the context of a legal system, where in such system is itself based upon this same set of basic, fundamental, or inalienable rights.

I found a very impressive, real and schoked video about the fundamental human rights. They all are real situations and stories.
CITIZENSHIP
The concept of the citizenship is based on the national appartenance.
It's when a person is recognize as a legal person in front of the law and the state, we call him a CITIZEN
(here come the rights and duties).
Moreover the citizenship is related to the NATIONALITY.
For example, if we are a citizen of an European country, we are also a citizen of the European Union.
Unfortunately this is a debate with very controverses. In 2006, the E.U was very famous and respectable but nowadays
it's very crtiticism.
The good point of view
European citizenship: The death of nations? (The bad point of view)